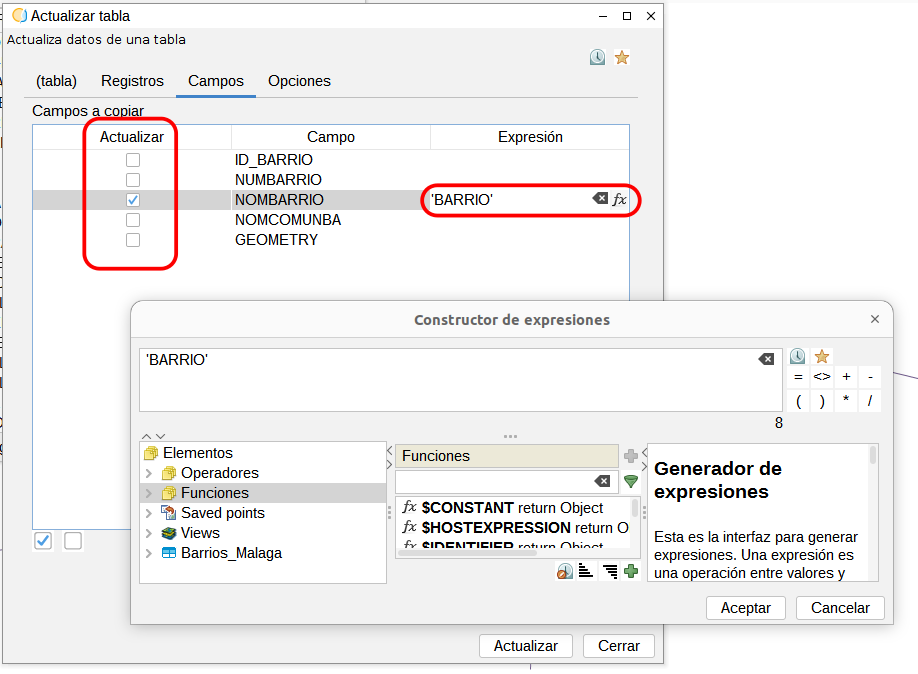
Ebbene sì, cara lettrice, anche nel 2025 ho letto, ho visto, ho guardato, ho ascoltato, ho fatto cose sia stando fermo dove ero sia muovendomi. Da un certo punto di vista tutto quello che segue in questo articolo è nullo perché il 2025 è stato l’anno di un blando ma importante risveglio dal torpore e sono andato alcune (o tante, punti di vista) volte in piazza a mettere il mio corpo per il popolo di Gaza. Ma da un altro punto di vista tutto quello che segue è esattamente quello che bisogna fare per non vendere le nostre vite allo stesso sistema che ci divora, ci rende complici. Nulla di tutto questo è intrattenimento, tutto è sbattimento, tutto è amore, tutto è rabbia.
I libri che mi sono piaciuti
Ho continuato a leggere Solenoide, di Mircea Cărtărescu (che anche quest’anno non ha vinto un nobel, ma che differenza fa). È un’opera monumentale, non solo per la sua estensione fisica ma anche per la tela che tesse, fatta di parti apparentemente semplici e anche marcatamente ripetitive. L’effetto complessivo però è ipnotico e travolgente. Troppo complesso da recensire in poche parole, nei diversi piani narrativi intreccia la letteratura, la scuola, l’infanzia, la visione al tempo stesso onirica e disincantata sulla città di Bucarest in una fatiscente quanto lontana dimensione politica… in un potentissimo labirinto tra Borges, Kafka, Lilian Ethel Voynich, il manoscritto dallo stesso nome… E lo consiglio vivamente anche se certe parti risultano un po’ ripetitive, o ostiche, o persino fastidiose da leggere.
A fine 2024 avevo fatto un prodigioso acquisto di fumetti da add. E ne ho letti molti. Tutti mi hanno detto qualcosa, per quanto molto diversi tra loro, e quindi lode alla casa editrice che spazia. Metto questi fumetti tutti insieme non perché abbiano tra di loro qualche cosa di particolare in comune ma perché non sono molto abituato alleggiere fumetti e anzi ho cercato di fare del mio meglio per imparare a leggere fumetti senza sfogliarli velocemente alla ricerca di una trama che molto spesso non c’è o non è per niente in primo piano. Quindi, per dire, Disfacimento è un viaggio onirico e quasi lisergico all’interno di un mondo che si muove in modo molto lento ma contemporaneamente anche con degli slanci molto crudi di un’umanità ibrida e totalmente intrisa di animale e vegetale. Oppure i due di M. S. Harkness, veramente molto molto dolorosi da leggere e con un sentimento cupo ma anche una fortissima voglia di vivere. Nuvole sul soffitto è molto amaro, soprattutto nelle parti in cui il protagonista si rapporta con la figlia e ha colpito molto duro. The End è stata fonte di grandissima riflessione, molto profondo e anche particolarmente struggente il modo in cui poi viene raccontato il progresso nella creazione del fumetto stesso. Grande Oceano è meraviglioso ho anche cercato di convincere mio figlio a leggerlo e ha la dimensione fiabesca, strepitosa di una grande avventura. Ma il fumetto che ho letto e riletto più volte, trovandoci ogni volta dei risvolti veramente potentissimi è Baby Blue che racconta una storia non più distopica e la affronta in un modo assolutamente esagerato ed epico. Prima dell’oblio è un piccolo labirinto narrativo in forma grafica, disincantato ma anche pieno di speranza su tutto quello che diamo per scontato delle nostre vite.
Non è della stessa provenienza la graphic novel Stretta al cuore di Stepánka Jislová, quindi ne parlo a parte. È veramente intenso e lascia senza parole in più punti. Sembra che parta come una storia individuale ma si costruisce come una vicenda molto più ampia, sugli stereotipi di genere anzitutto ma anche sulle difficoltà familiari, sugli abusi sessuali, sui traumi che lasciano sempre un segno.
Il calcio del figlio di Wu Ming 4 mi è stato regalato ed è una lettura necessaria per chi come me si trova a fare involontariamente il genitore di giovanissimi calciatori. Dà speranza, in uno spazio in cui c’è tanto bisogno di averne perché spesso tutto sembra compresso tra desiderio di primeggiare individualmente in uno sport ostinatamente di squadra, senso di appartenenza, movimento fisico di corpi nello spazio.
Tiarè di Célestine Hitiura Vaite potrebbe sembrare una lettura leggera ma non lo è. Il fatto che sia ambientato in un mondo familiare e domestico, anche se geograficamente lontanissimo, lo rende universale. Riporto una bella citazione che mi è rimasta impressa
Materena ripone l’olio per friggere, ricorda il discorso fatto alla madre pochi giorni addietro: che nella prossima vita forse tornerà come lesbica.
Al che, sua madre ha commentato: «Perché aspettare?».
Ah, oui, alors. Perché aspettare?
Tiaré, pagina 63 dell’edizione italiana
Da Eleuthera ho comprato due libri di James C. Scott tradotti in italiano. Il dominio e l’arte della resistenza mi ha tenuto compagnia per buona parte dell’anno. È una lettura piacevole, molto istruttiva, e ha una visuale molto ampia sul tema, il quale di per sé non è frequente come frame di comprensione dei fenomeni sociali, né antichi né contemporanei. Non è un manuale sull’arte della resistenza, ma comunque ne fa un trattato piuttosto ricco. Lo sguardo dello stato mi ha accompagnato tutta l’estate. Molto pacato e lucido, capace di abbracciare tematiche apparentemente lontanissime tra loro con una visione molto coerente. La postilla finale di commento all’edizione italiana è un preoccupante aggiornamento al ventunesimo secolo della traiettoria descritta da Scott.
Un oggetto narrativo non identificato è Prompt di fine mondo di Agnese Trocchi del collettivo CIRCE. Liberatorio e libero, c’è bisogno di più opere con questo tipo di spazio di manovra.
Mi aveva attirato il titolo de La vegetariana di Han Kang, premio Nobel. Il libro è diviso in tre parti. Ogni parte è narrata dal punto di vista di un personaggio diverso e fortemente centrata sul rapporto tra personaggio (marito, cognato, sorella) e “la vegetariana” vera protagonista della storia. Uno sviluppo in parte circolare che nelle pagine conclusive sembra tornare all’inizio e dare un senso possibile, uno dei diversi possibili, alla vicenda inquietante e drammatica. E proprio nella conclusione mi sembra di trovare una via d’uscita dove viene mostrata la vera tragedia, quella di tutta la violenza subita, perciò la progressiva vegetalizzazione è liberazione. Molto intenso. La seconda parte sembra dare un risvolto positivo, creativo, per quanto folle, ma si conclude sia malamente rispetto a queste velleità sia raggiungendo un punto di non ritorno.
Ho voluto approfondire l’opera di Han Kang con L’ora di greco. Purtroppo l’ho letto una prima volta troppo in fretta, troppo trascinato da una trama che non c’è, e mi trovo in preda a una sensazione di dolore e sconvolgimento. L’ho riletto più lentamente. Il libro diventa via via più lirico, più criptico, ma trasmette comunque un senso di distacco tragico che sembra universale: distacco dalla famiglia, distacco dalla vista, distacco dalla parola, distacco dall’umano. In questo risiede il legame con “La vegetariana” a mio avviso, insieme al fatto che il fulcro di tutto questo dolore e distacco si trova nel nucleo familiare. È un testo difficile, almeno lo è stato per me. C’è una sottile via di uscita, se non di speranza.
Leggendo La straniera di Claudia Durastanti, ho capito che tutta la prima parte di libro mi sembra ricalcare “Middlesex” di Jeffrey Eugenides (un libro che adoro), non in modo esplicito ma tutta l’epopea degli avi, la migrazione, essere chi sei perché quella è la tua storia. Tuttavia questo libro non mi è piaciuto molto nel complesso, diversamente dagli altri che non mi sono piaciuti ne parlo perché apprezzo molto Claudia Durastanti come traduttrice…
e Brevemente risplendiamo sulla terra di Ocean Vuong è esattamente un libro che Durastanti ha tradotto. Insolitamente (per me) diretto e tagliente, ma con una profondità fortissima. Difficile dire che l’ho compreso tutto. Sicuro che mi ha fatto sentire cose mai viste prima, potentissime. Una scrittura senza steccati, ardente.
Le mostre
In primavera siamo andati a Ferrara per la mostra di Alphonse Mucha, c’era accoppiata anche quella di Giovanni Boldini, entrambe a Palazzo dei Diamanti. Non paragonabili se non nella mente dei venditori di biglietti. Mucha gira molto in mostre commerciali come questa, la sua arte libera un’immaginario al tempo stesso fuori dal tempo e molto situato, quasi imprigionato nella tela su cui è stato dipinto.
A Genova, ho visto a Palazzo Ducale Jacopo Benassi Libero! e mi ha colpito molto, una grande libertà e affronto alla morale artistica. Ho visto sempre al Ducale anche altre mostre tra cui quella su Lisetta Carmi, che ho apprezzato molto anche perché non era risicata negli spazi e Meriggiare pallido e assorto, fotografica contemporanea che ho trovato di poca anima e molto bisognosa di un’interpretazione totalmente assente. THE OTHER DIRECTION invece mi sembra degna di nota perché tratta un tema intersezionale da un punto di vista originale: voci di donne su una linea di autobus urbano che attraversa mezza città, interi quartieri e periferie – è la linea 1 che prendo spesso anche io.
Inoltre al Castello D’Albertis ho visto World Things Genova che accoppia mostra fotografica con etnografia contemporanea, attualizzazione post-coloniale delle collezioni del museo con presente di migrazioni.
I podcast
Ho ascoltato veramente molto meno rispetto allo scorso anno. A settembre ho anche iniziato ad accusare i primi sintomi di un acufene abbastanza intenso.
Ho proseguito in modo spezzato Il mondo, Stories e Love Bombing. Ho ascoltato alcuni episodi de Le comari dell’arte, molto liberatorie, di Nuovo baretto utopia con le registrazioni di kenobit, di Mordicchio non l’ha mai detto che purtroppo mi pare interrotto. Fare un podcast è dura.
Ho scoperto il favoloso L’orda d’oro, che è frutto di un programma radiofonico su Radio Onda Rossa. Parla dell’Asia centrale, in un numero altamente soddisfacente di diverse manifestazioni e punti di vista, sempre sostenuti da musica di generi diversi.
Le serie
Ho iniziato a guardare Anatane e i ragazzi di Okura su Rai Play, una serie animata franco-canadese ambientata in un futuro (?) distopico. Episodi semplici e brevi che ho trovato piacevoli.
Cyberpunk: Edgerunners è piuttosto semplice e violento, ma la grafica e la colonna sonora sono molto buone. Un giorno ho guardato un episodio e poi ho scoperto che era quello finale, ma mi è parso un po’ troppo tirato via, anche se l’ultima scena è molto commovente.
Ho guardato 3 minuti della prima puntata di Stranger things. Non so se conta.
Il teatro
Nella prima parte dell’anno sono andato alcune volte a teatro, sempre meno di quanto vorrei.
Lo strepitoso D’oro. Il sesto senso partigiano è stato fortissimo a partire dalle prime battute fuori dal palco, con i primi dodici articoli della Costituzione recitati a piena voce da un gruppo di giovani. Storie vere di uomini e donne che ci hanno tramandato gesti apparentemente semplici di libertà, quando questa era impossibile.
Stabat mater di Liv Ferracchiati è uno sguardo sulla mascolinità e sulle aspettative del genere, della coppia raccontato in modo leggero e divertente, ma al tempo stesso serissimo. Bello il dibattito finale con l’autrice, le altre attrici e Vera Gheno.
La musica
Sono andato a diversi concerti! Il 24 aprile al circolo ARCI Perugina di Certosa ho ascoltato i canti anarchici e partigiani dei Mars on Pluto, e (per me) soprattutto dei Cocks, una punk rock band di Sampierdarena che incarna molto di quello che avrei voluto fare tanti anni fa con altri sgangherati di periferia.
Ho partecipato alla prima serata di Electropark, un festival di musica elettronica che si tiene da 15 anni a Genova. Le artiste della serata erano Tadleeh, la genovese Ginevra Nervi e Luxe da Londra. Sono fuori dai miei confini con la musica elettronica ma ho apprezzato l’atmosfera molto rilassata e contemplativa.
Sono andato a un concerto rap alla Libera collina di Castello, mi è piaciuta la grande energia de La cercleuse, collettivo rap femminista francese.
Con Elisa sono andato al concerto di Vinicio Capossela, non era la prima volta ed è sempre più forte il modo in cui lui e le persone sul palco con lui usano la musica per raccontare storie.
I viaggi
A giugno siamo tornati a Creta, dopo ben 10 anni! Lo abbiamo fatto con il più improbabile dei mezzi di trasporto, cioè la nostra automobile, traghettata attraverso Adriatico ed Egeo dalle fedeli navi che conosciamo da 20 anni. È stato un viaggio intenso ma molto bello, abbiamo fatto base fissa a Kalamaki e poi girato un po’ nella zona di Creta centrale.
In primavera eravamo andati a Ferrara, oltre alle mostre abbiamo passeggiato per la città, trovato parchi dove riposare all’ombra, ottime gelaterie, ristoranti coreani, tantissime biciclette.
Sono andato per lavoro due giorni a Venezia, riuscendo a fare una veloce visita alle gallerie dell’Accademia con tanto di mostra che includeva L’uomo vitruviano lì conservato. Ma è proprio un piacere enorme essere a Venezia e basta.
In estate abbiamo fatto una vacanza in provincia di Cuneo. Abbiamo iniziato con una tappa a Molare da Franco B. famoso cantautore genovese ed ex collega, con bagno nel torrente. Facciamo base a Villar San Costanzo, patria dei ciciu e del famoso biscottificio che macina la farina nel mulino di Dronero lì vicino. Siamo andati a Entracque a visitare il centro sui lupi, ai bambini è piaciuto molto.
In autunno ho iniziato un corso di speleologia, ma questa è un’altra storia.









 Call for Papers
Call for Papers Submit your proposal:
Submit your proposal:  Call for Sponsors
Call for Sponsors About the User Conference
About the User Conference About the Contributor Meeting
About the Contributor Meeting




























 Time for a rethink – “You can’t always get what you want”
Time for a rethink – “You can’t always get what you want” – “But if you try sometimes ..”
– “But if you try sometimes ..”
















































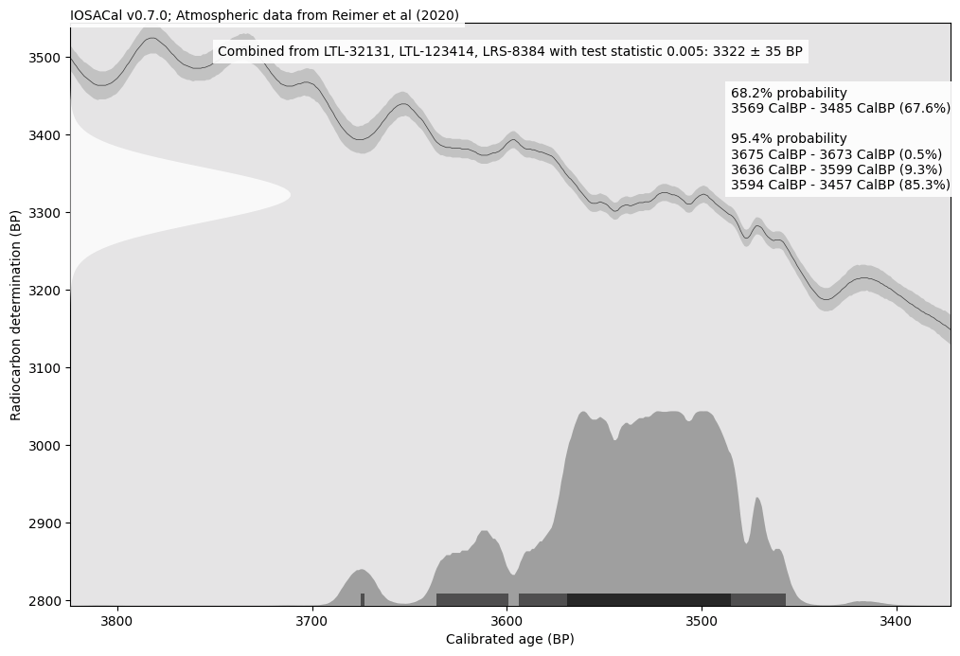 One of the standard plots rendered in the latest IOSACal version. It looks exactly as before.
One of the standard plots rendered in the latest IOSACal version. It looks exactly as before.







 O que você vai dominar:
O que você vai dominar: Python do zero com foco técnico
Python do zero com foco técnico Para quem é este curso?
Para quem é este curso? Profissionais de GIS e Geoprocessamento
Profissionais de GIS e Geoprocessamento Não é curso raso.
Não é curso raso. Vagas limitadas
Vagas limitadas